What is firewall? A firewall is one of the most essential network security tools, designed to monitor and control incoming and outgoing traffic based on predefined rules. Acting as a virtual gatekeeper, it helps safeguard your private network from external threats. Despite its importance, many users make common mistakes in configuring and managing firewalls, leaving their systems vulnerable. Let’s explore what a firewall is, how it works, and how you can avoid these pitfalls to ensure your network is fully protected.
Learn more: How to Send Secure Emails & Protect Privacy
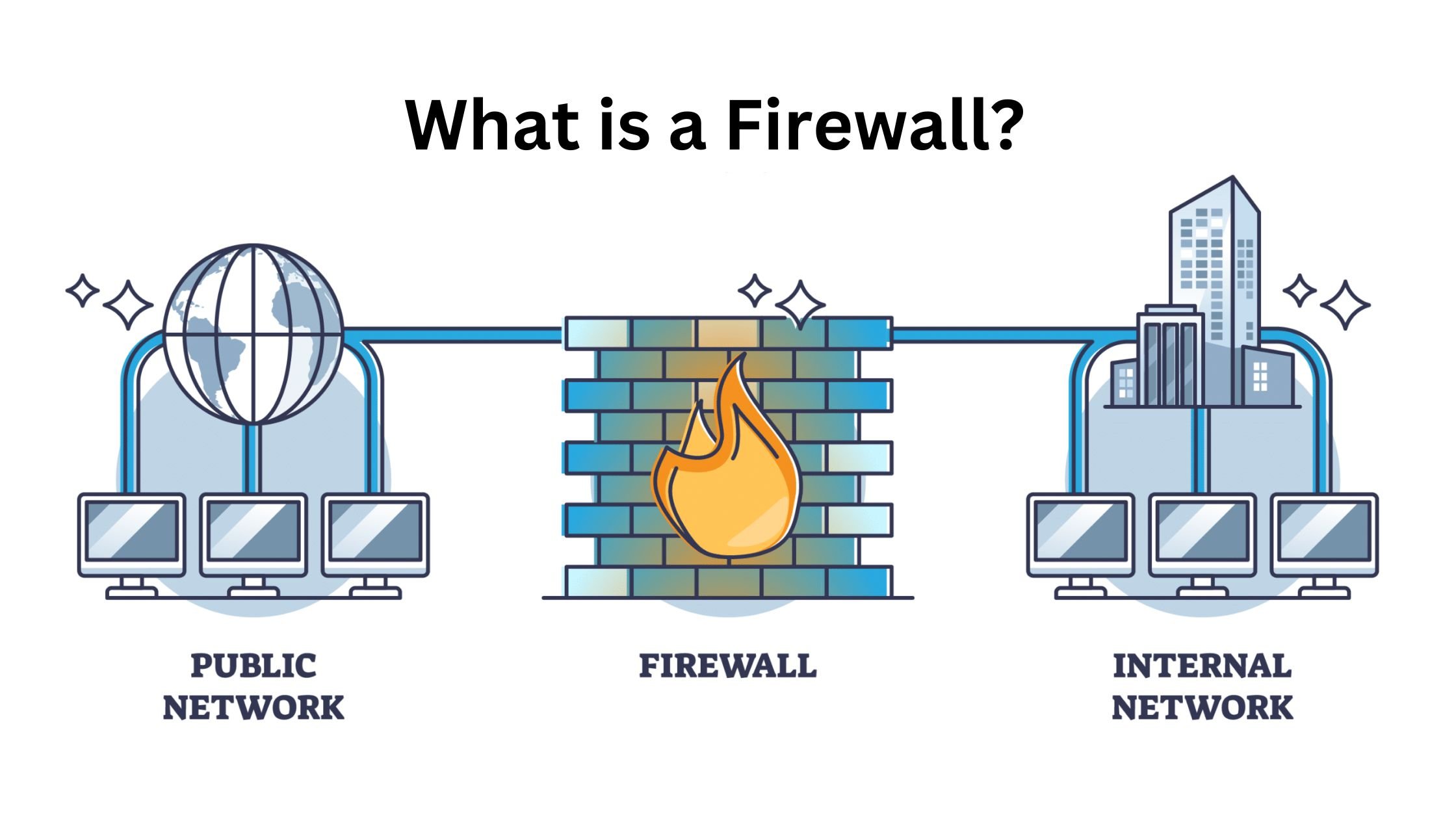
What is a Firewall?
What is firewall? A firewall is a network security system designed to monitor and control traffic coming into or going out of a private network. Think of it as a protective gatekeeper that checks all network activity and decides whether to allow it through based on preset rules.
The Origin of the Term “Firewall”: The term “firewall” comes from real-world firewalls — physical walls built to stop or slow the spread of fire in buildings. Similarly, in cybersecurity, firewalls are designed to stop or slow down the spread of online threats like viruses, hackers, or unauthorized access.
In today’s world, firewalls are essential for both personal and business networks. They can be hardware-based, software-based, or a combination of both. Modern firewalls, often called next-generation firewalls (NGFW), also provide advanced features like intrusion prevention, malware filtering, and deep traffic inspection to stop complex cyberattacks.
How does a Firewall work?
A firewall acts as a protective gate, controlling and filtering network traffic entering or leaving a system. It serves as a barrier, distinguishing between “trusted” and “untrusted” data, thereby preventing potential external threats.
Basic Operating Principles:
- Traffic Segmentation: Firewalls establish control points, often referred to as “choke points,” where network traffic is evaluated based on predefined rules. Only data meeting specific criteria is permitted to pass through.
- Connection Analysis: Firewalls examine the source, destination, content, and protocols of data packets before deciding whether to allow or block them.
By implementing these measures, firewalls play a crucial role in maintaining network security, ensuring that only authorized communications occur while blocking potential threats.
Learn more: How to Remove Personal Information From the Internet

Top 6 Popular Types of Firewalls and How They Are Classified
What is firewall? Firewalls are essential tools in network security, protecting systems by controlling and filtering traffic. Firewalls can be categorized based on their operation, filtering methods, and ability to monitor connections. Here are the 6 main types of firewalls and how they work.
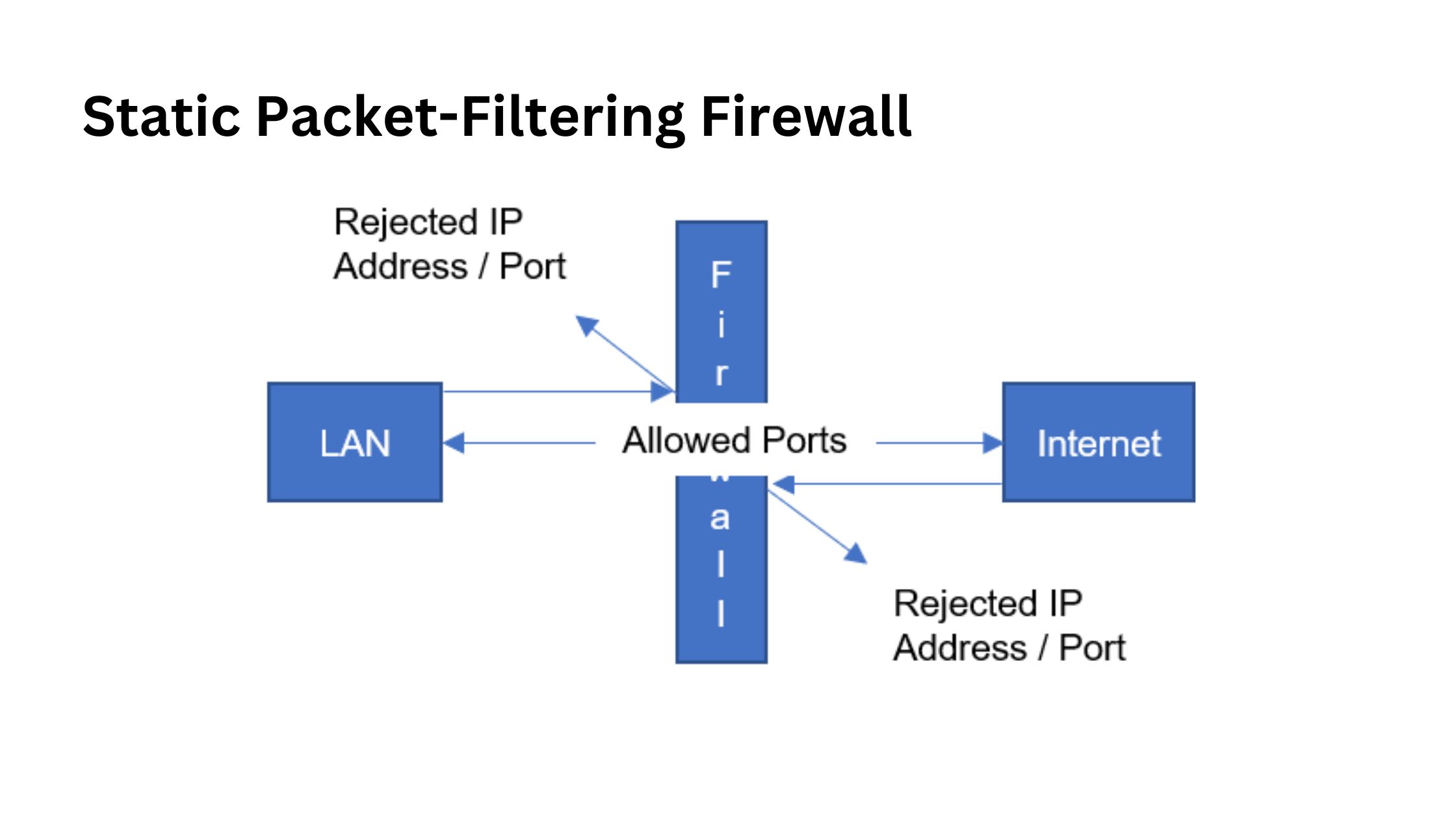
Static Packet-Filtering Firewall
- How it works:
This firewall examines individual data packets at the network layer (Layer 3) of the OSI model. It checks the IP address, port number, and protocol but does not track past connections. - Advantages:
- Simple and easy to set up.
- Effective for small networks with basic security needs.
- Disadvantages:
- Cannot inspect packet contents.
- Does not monitor active connections, leaving it vulnerable to advanced attacks.
Interesting Fact: While static packet-filtering firewalls are foundational, their simplicity is no match for modern attacks like IP spoofing, where attackers disguise their IP address to bypass basic filters.
Circuit-Level Gateway Firewall
- How it works:
Operating at the session layer (Layer 5), this firewall verifies the legitimacy of connections before allowing them to remain open. It ensures that the connection is “trusted” but does not inspect the actual data being transmitted. - Advantages:
- Easy to implement and fast performance for high-speed connections.
- Disadvantages:
- Does not monitor traffic after a connection is established.
- Vulnerable to misuse if attackers gain access through an approved connection.
Did You Know? Circuit-level gateways are often used as a secondary layer of defense alongside other firewalls to optimize security without sacrificing speed.
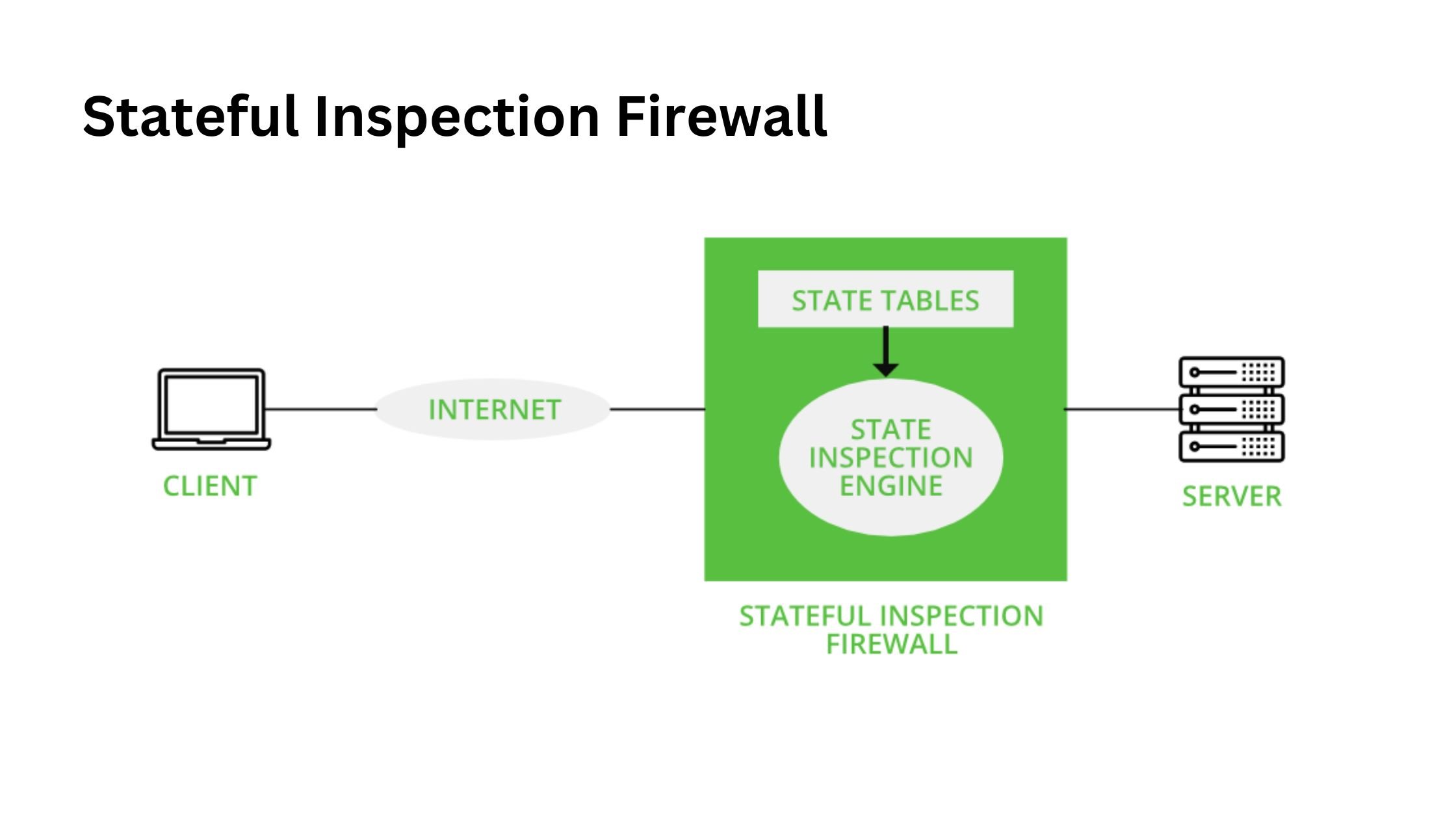
Stateful Inspection Firewall
- How it works:
Also known as dynamic packet filtering, this firewall operates across multiple layers, including the application layer (Layer 7). It monitors ongoing connections and remembers past traffic using a state table to make filtering decisions. - Advantages:
- Continuously tracks connections for greater security.
- Adapts to patterns and learns from previous threats.
- Disadvantages:
- More complex to configure and manage.
- Requires more resources compared to basic firewalls.
Insight: Most modern firewalls use stateful inspection as a core feature because it offers a balance between performance and security.
Proxy Firewall (Application-Level Firewall)
- How it works:
Acting as an intermediary between internal and external networks, proxy firewalls filter traffic at the application layer. They analyze data for specific protocols like HTTP, FTP, and DNS for deeper inspection. - Advantages:
- Provides high security by examining data content.
- Ideal for systems that demand strict access control.
- Disadvantages:
- Can slow down data transmission.
- May require additional resources to manage.
Example: Proxy firewalls are widely used in enterprises to filter web traffic and block malicious requests before they reach the network.
Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW)
- How it works:
NGFWs combine the features of traditional firewalls with advanced security technologies like intrusion prevention systems (IPS) and deep packet inspection (DPI). They are designed to detect and block advanced threats like malware and ransomware. - Advantages:
- Identifies and prevents advanced security threats.
- Suitable for enterprises and large, complex networks.
- Disadvantages:
- High cost compared to traditional firewalls.
Fun Fact: NGFWs often include AI-based threat detection to identify zero-day attacks—new vulnerabilities not yet discovered or patched.
Hybrid Firewall
- How it works:
Hybrid firewalls combine two or more firewall types, such as stateful inspection and proxy firewalls, to deliver comprehensive protection. These systems are common in large networks with diverse security needs. - Advantages:
- Maximizes security by leveraging multiple firewall technologies.
- Customizable for complex systems.
- Disadvantages:
- Requires expert knowledge to configure and maintain.
- Can be resource-intensive.
Insight: Hybrid firewalls are often used in organizations that require layered defense strategies, ensuring no single vulnerability exposes the entire network.
5 Common Firewall Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Firewalls play a critical role in network security by filtering and controlling traffic to prevent potential threats. However, improper use can make firewalls ineffective or even leave severe security vulnerabilities. Here are the 5 most common mistakes people make when using firewalls and how to fix them.
Misconfiguring Filtering Rules
Firewalls rely on filtering rules to allow or block traffic. However, many users either stick to default configurations or fail to customize rules properly. This can result in:
- Blocking valid, trusted connections.
- Allowing unauthorized traffic, creating a security loophole for external attacks.
Solution:
- Regularly review and update filtering rules to match your organization’s current needs.
- Avoid overly restrictive or too lenient configurations. For example, ensure only necessary ports and IP addresses are permitted while blocking everything else as a precaution.
Insight: Misconfigured firewalls account for over 99% of firewall breaches, according to Gartner. Regular audits and clear rule structures are essential for securing networks.
Relying Solely on Firewalls for Network Protection
Firewalls are powerful tools, but they cannot block every threat, especially:
- Insider threats within internal networks.
- Malware and malicious software disguised within trusted connections or downloads.
Solution:
Combine firewalls with other security measures:
- Antivirus software to detect malware and ransomware.
- Network monitoring systems to detect unusual behavior.
- Data encryption to secure sensitive data.
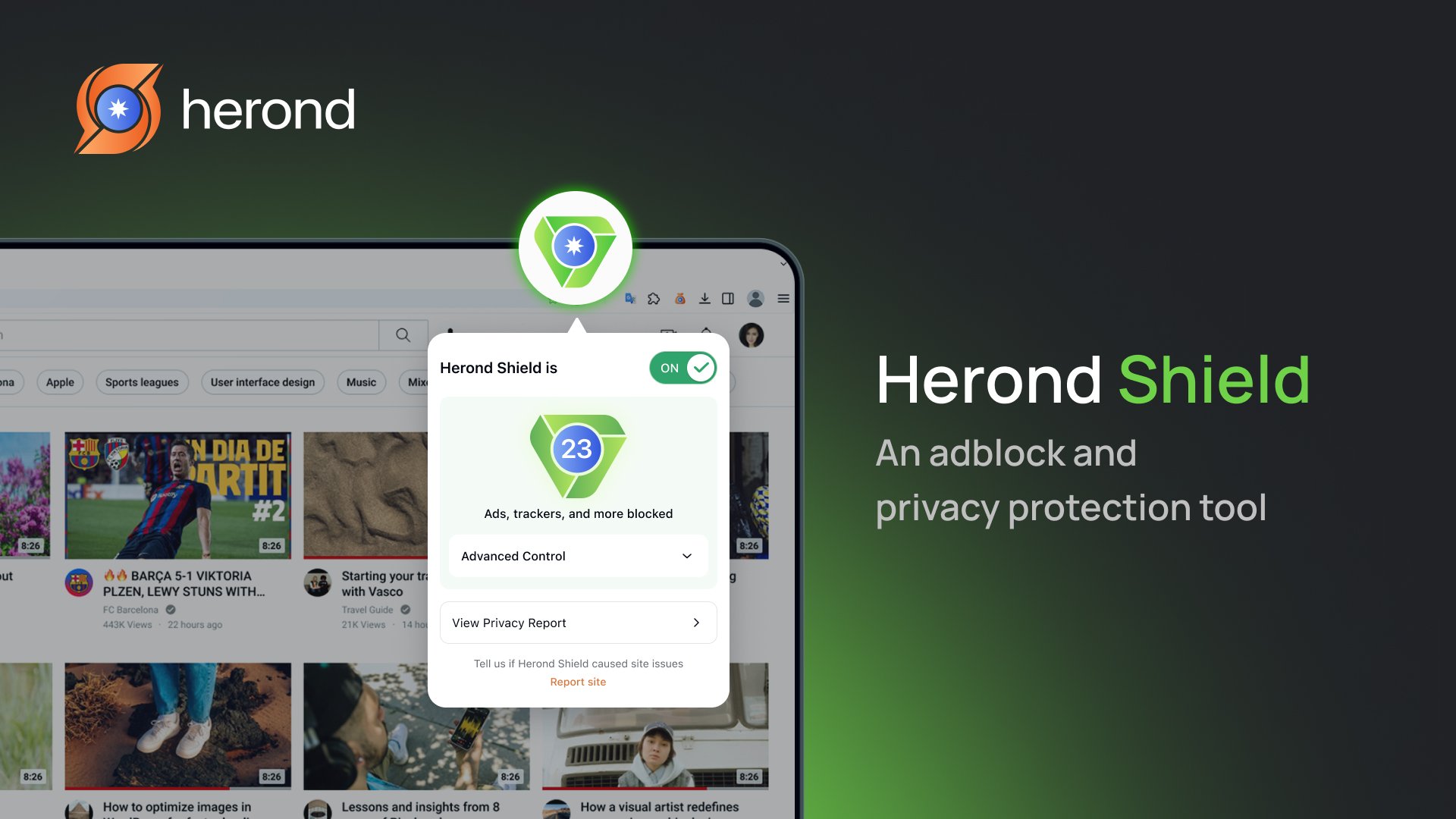
Additionally, consider using tools like Herond Browser to protect against malware downloads.
Herond Browser’s Technology:
- Herond Shield: Blocks ads, trackers, and malware across all websites, including social media and streaming platforms, ensuring a clean and safe browsing experience.
- Advanced Security Alert System (ASAS): Automatically detects and warns users about phishing or fake websites.
- Speed Optimization: By blocking unnecessary scripts, Herond improves browsing speeds up to 3x faster while reducing system resource usage.
Herond Browser is a valuable addition to your security stack, helping minimize malware risks. You can download it for free on Google Play or the App Store.
Failing to Monitor and Update the Firewall Regularly
A firewall without regular updates is like a locked door with a broken key. It won’t protect you from new or evolving threats. Common mistakes include:
- Ignoring software and firmware updates.
- Overlooking firewall audit logs or ignoring alerts.
Solution:
- Schedule regular updates for firewall firmware and software to stay protected against the latest vulnerabilities.
- Monitor firewall logs and alerts to spot suspicious activity early.
- Automate reporting tools to save time and improve efficiency.
Fun Fact: Cybersecurity firm Check Point reported that outdated firewalls leave systems vulnerable to 75% of new cyberattacks. Regular updates can close these gaps.
Not Using Internal Firewalls
Many businesses rely only on external firewalls, ignoring internal network protection. This leaves significant security gaps if a threat bypasses the perimeter firewall, such as:
- Employees clicking on malicious links.
- Hackers taking control of a device inside the network.
Solution:
Implement host-based firewalls on individual endpoints like laptops, desktops, and servers to monitor traffic within the internal network. This ensures that even if external defenses fail, internal systems remain protected.
Not Verifying “Allowed” Connections
Not all permitted connections are safe. Even legitimate-looking traffic can carry hidden threats like:
- IP spoofing: Attackers disguise their IP address to appear trustworthy.
- Compromised services: Applications or systems infected with malware can create backdoors for hackers.
Solution:
- Use advanced threat detection tools to analyze permitted connections in real time.
- Upgrade to Next-Generation Firewalls (NGFW), which offer deep packet inspection and identify hidden threats.

Conclusion
What is firewall? A firewall is a vital component in network security, offering robust protection against external threats. However, to maximize its effectiveness, it’s crucial to use it correctly and pair it with other security measures like antivirus software and data encryption. Regular updates, monitoring, and advanced tools such as Herond Browser can further enhance your system’s defenses, providing a safer and more seamless online experience.
About Herond Browser
Herond Browser is a cutting-edge Web 3.0 browser designed to prioritize user privacy and security. By blocking intrusive ads, harmful trackers, and profiling cookies, Herond creates a safer and faster browsing experience while minimizing data consumption.
To enhance user control over their digital presence, Herond offers two essential tools:
- Herond Shield: A robust adblocker and privacy protection suite.
- Herond Wallet: A secure, multi-chain, non-custodial social wallet.
As a pioneering Web 2.5 solution, Herond is paving the way for mass Web 3.0 adoption by providing a seamless transition for users while upholding the core principles of decentralization and user ownership.
Have any questions or suggestions? Contact us:
- On Telegram https://t.me/herond_browser
- DM our official X @HerondBrowser
- Technical support topic on https://community.herond.org