In the rapidly evolving world of technology and digital economies, understanding the forces that drive value and growth is essential. One such force is Metcalfe’s Law, which posits that the value of a network increases exponentially as more users connect. Originally formulated by Robert Metcalfe, this principle is particularly significant in the realm of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technologies, where the success of a project often depends on its ability to attract a growing user base. This article aims to explore Metcalfe’s Law, its implications in the crypto space, and the various network effects it encompasses, highlighting why these dynamics are crucial for anyone navigating the complexities of digital networks.
What is Metcalfe’s Law?
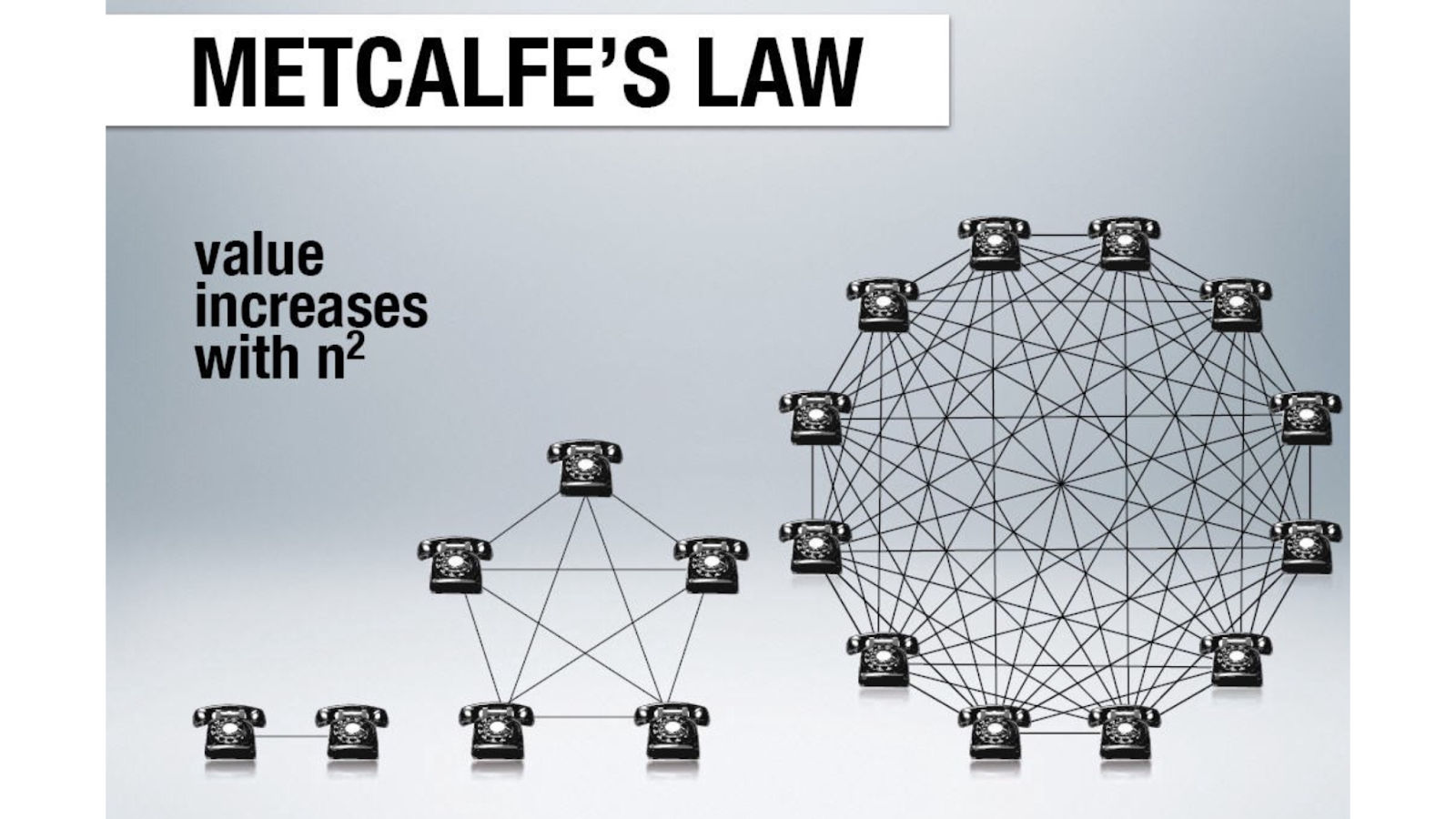
Metcalfe’s Law is a principle that describes how the value of a network grows as more users or devices connect to it. Proposed by Robert Metcalfe, the co-inventor of Ethernet, it states that the value of a network is proportional to the square of the number of its users, represented as:
𝑉∝ 𝑛2
where:
𝑉: is the network’s value,
𝑛: is the number of users (or nodes) in the network.
The core idea is that as each new participant joins a network, they add value not just by their own participation but also by enabling all other users to connect with them. This results in exponential growth in network value, as each connection adds potential interactions between users.
Types of network effects in crypto
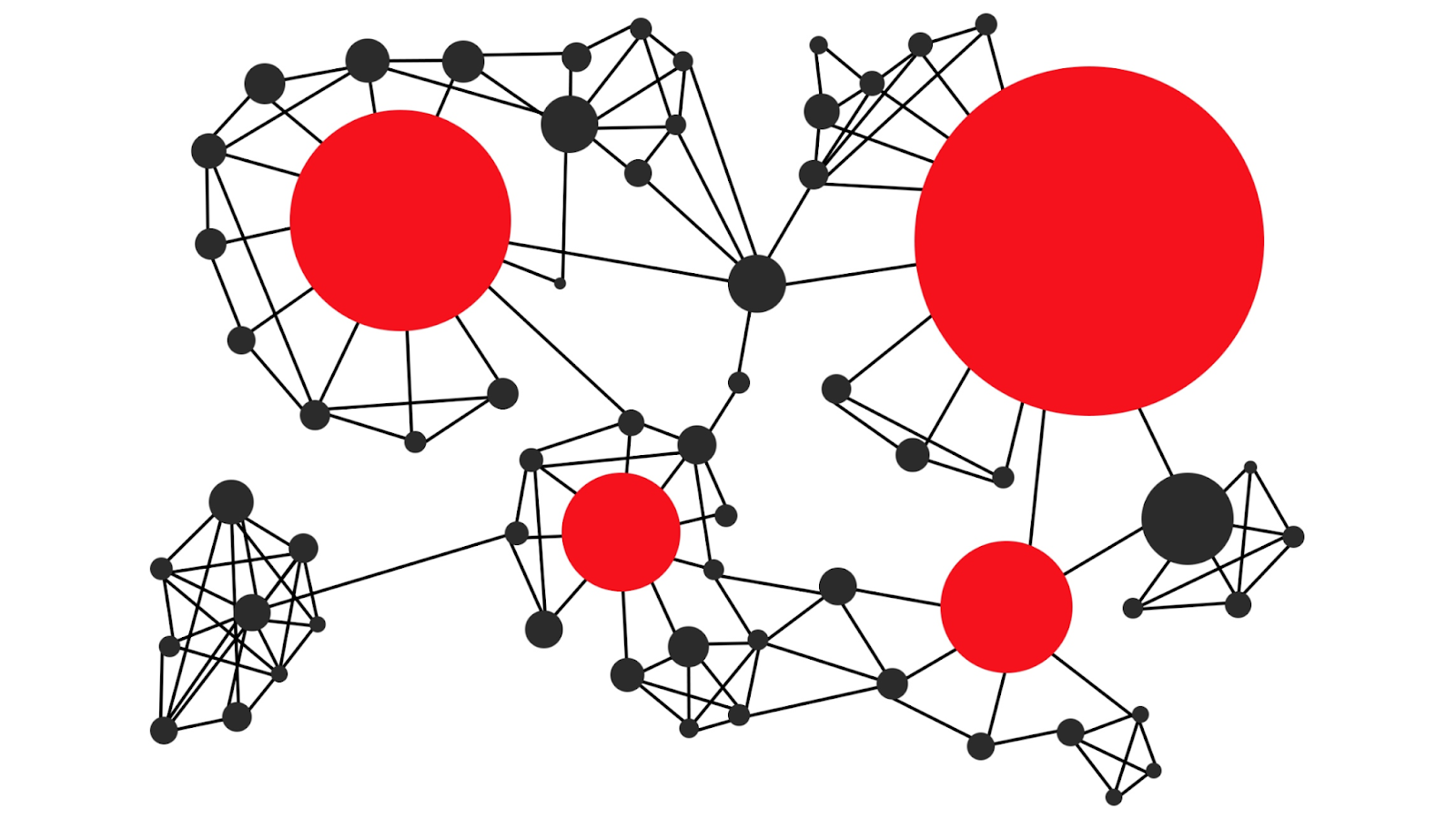
Metcalfe’s Law provides a way to quantify how network value scales with the number of participants, which directly ties into the various types of network effects found in crypto. In this context, each type of network effect contributes to the overall growth and value of a blockchain network, which Metcalfe’s Law models as increasing proportionally to the square of the number of users. Here’s how different types of network effects in crypto can be understood through Metcalfe’s Law:
Direct Network Effects
Connection to Metcalfe’s Law: Metcalfe’s Law directly applies to direct network effects by suggesting that each new user increases the network’s value exponentially. As more participants join and interact, the number of possible connections between them grows, enhancing the network’s overall value.
Example: In Bitcoin, each additional user creates more transaction opportunities and liquidity, increasing the network’s value for all other users, as Metcalfe’s Law predicts.
Indirect Network Effects
Connection to Metcalfe’s Law: Indirect network effects involve the development of complementary products or services, which boost the network’s utility and attract new users. While these effects aren’t directly about user connections, Metcalfe’s Law still applies in the sense that as more users join, the demand for complementary products grows, increasing the network’s overall value.
Example: In Ethereum, more users and developers build dApps and DeFi protocols, which increase Ethereum’s value indirectly. Metcalfe’s Law helps explain this by illustrating that as users grow, so does the attraction to build within the ecosystem, multiplying Ethereum’s value.
Data Network Effects
Connection to Metcalfe’s Law: As more users join, the network generates more data, which can be analyzed to improve network performance, security, and user experience. This self-reinforcing cycle aligns with Metcalfe’s Law by showing that the value derived from data increases exponentially as user numbers grow.
Example: A blockchain like Solana, which processes large amounts of data, uses insights to optimize transaction processing. As more users and transactions increase data volume, the network’s functionality and value for future users improve in line with Metcalfe’s Law.
Two-Sided Network Effects
Connection to Metcalfe’s Law: Two-sided networks benefit from Metcalfe’s Law because both sides (e.g., traders and liquidity providers) increase the value of the network as they grow. Each new user on one side (e.g., traders) increases the utility for users on the other (e.g., liquidity providers), driving exponential network value.
Example: In DeFi platforms like Uniswap, each liquidity provider attracts more traders and vice versa. Metcalfe’s Law explains the growth of network value here as each new participant on either side enhances opportunities and utility for all other participants.
Developer Network Effects (Technological Network Effects)
Connection to Metcalfe’s Law: The value of a network also grows as more developers join and contribute code, applications, and improvements. Metcalfe’s Law applies here in that as the developer base grows, each developer’s contributions add to the network’s utility, attracting even more developers and users.
Example: Ethereum’s extensive developer community has created an ever-growing library of dApps and protocols, which increases Ethereum’s utility and market value. The value of this ecosystem, supported by Metcalfe’s Law, grows exponentially with each additional developer and user who benefits from the network’s applications.
Why does Metcalfe’s Law matter in crypto?
Here are some of the main reasons Metcalfe’s Law matters in crypto:
Exponential Value Growth with User Adoption
According to Metcalfe’s Law, the value of a network is proportional to the square of the number of its users. In the context of crypto, as more users join a blockchain network, the total potential value grows exponentially because each new user creates more possible connections and interactions.
Increased Liquidity and Trading Volume
In cryptocurrency markets, liquidity and trading volume are essential for price stability, user experience, and overall network health.
Metcalfe’s Law illustrates how liquidity and volume can increase exponentially as the user base grows. This positive cycle helps larger networks become more liquid and stable, making them more attractive to new participants.
Enhanced Network Security
In Proof-of-Work (PoW) and Proof-of-Stake (PoS) blockchains, security grows as more participants (miners or stakers) join the network. A larger, more decentralized network is more secure and less susceptible to attacks. In the end, it increases trust and encourages more users to participate.
Metcalfe’s Law shows how security network effects can grow as more users join. In more detail, it illustrates that each participant adds exponentially to the network’s resilience. This helps explain why established networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum have become more secure over time. Therefore, they help to increase their appeal to new users and investors.
Ecosystem Development and Innovation
Many blockchain networks benefit from developer activity and the creation of complementary applications (dApps, DeFi, NFTs, etc.), which further increase the network’s utility and user appeal.
Metcalfe’s Law suggests that as a network grows, its potential for innovation and new applications expands exponentially. For example, Ethereum has attracted an extensive ecosystem of developers who build on the network. Consequently, it enhances Ethereum’s value and attracts more users and developers in turn.
User Trust and Brand Strength
A large user base contributes to a network’s brand, reputation, and trustworthiness. Networks that reach a critical mass often become synonymous with reliability, which encourages even more adoption.
Metcalfe’s Law provides a framework for understanding how trust and brand value can grow exponentially with user numbers. Bitcoin benefits from this brand effect, making it a preferred choice for both new and experienced users.
“Winner-Takes-All” Dynamics
Metcalfe’s Law also explains why many markets, especially digital ones, tend to favor one or a few dominant players. Therefore, it consequently creates a “winner-takes-all” effect. In crypto, networks that grow quickly tend to attract more users and developers, further reinforcing their position.
This dynamic helps explain why Bitcoin and Ethereum have maintained market dominance despite the presence of thousands of alternative cryptocurrencies.
Limitations of Metcalfe’s Law
While Metcalfe’s Law provides a useful framework for understanding how network value scales with the number of participants, it has limitations, particularly when applied to complex, real-world networks like cryptocurrency and social networks. Here are some key limitations of Metcalfe’s Law:
- Equal Value Assumption: Assumes all user connections are equally valuable, which is often unrealistic.
- Ignores Scalability Issues: Doesn’t account for network congestion or resource limitations that reduce usability.
- Excludes Quality and Engagement: Considers only user count, not quality or engagement levels, which can impact real value.
- Assumes Positive Connections: Treats all interactions as beneficial, ignoring negative ones like spam or fraud.
- Oversimplifies Growth Patterns: Assumes steady exponential growth, overlooking fluctuations and stages of network development.
- Risk of Overvaluation: Can lead to overvalued networks if user count alone is used in financial models without considering other factors.
- Misses Interoperability Value: Treats networks as isolated, not accounting for value added through cross-network interactions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Metcalfe’s Law provides a crucial framework for understanding the exponential growth potential of networks, particularly in the dynamic realm of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technologies. By emphasizing the importance of user connections, this principle clarifies why some networks thrive while others struggle. The various network effects demonstrate how value accumulates with user participation. Understanding Metcalfe’s Law empowers investors, developers, and users to make informed decisions in a competitive landscape, helping them identify promising projects and navigate the complexities of the digital age. Embracing these principles is essential for anyone looking to succeed in the ever-evolving crypto space.
About Herond Browser

Herond Browser is a Web browser that prioritizes users’ privacy by blocking ads and cookie trackers, while offering fast browsing speed and low bandwidth consumption. Herond Browser features two built-in key products:
- Herond Shield: an adblock and privacy protection tool;
- Herond Wallet: a multi-chain, non-custodial social wallet.
Herond aims at becoming the ultimate Web 3.0 solution, heading towards the future of mass adoption. Herond has now released the mobile version on CH Play and App Store. Join our Community!