Typically, the first option for interacting with crypto is through cryptocurrency exchange platforms. Literally, these are an online marketplace where users can buy, sell, and trade cryptocurrencies. These platforms facilitate the exchange of digital assets by matching buyers with sellers and executing transactions.
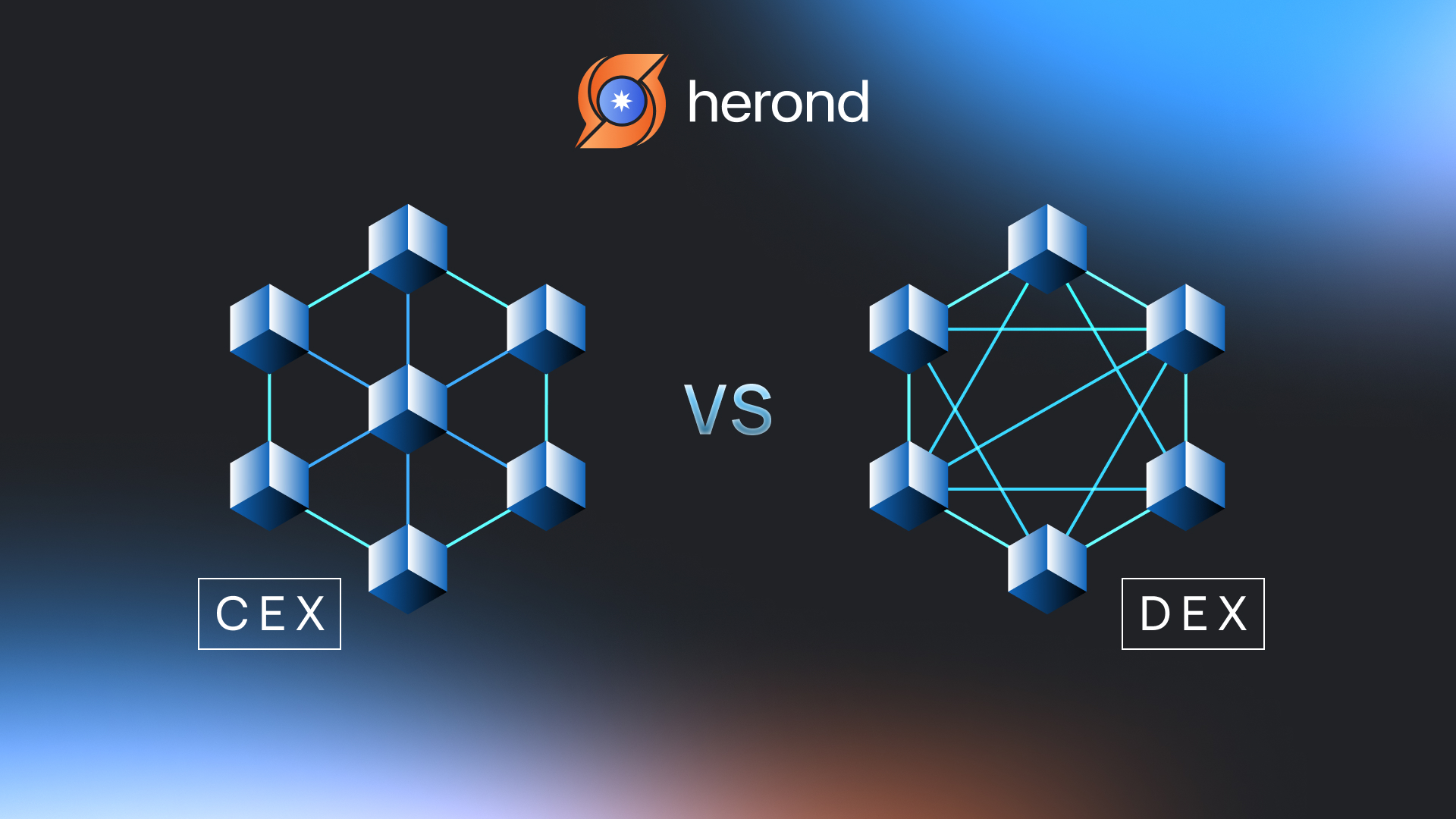
There are two types of cryptocurrency exchange platforms. Overall, Centralized Exchanges (CEX) and Decentralized Exchanges (DEX) have several key differences, which impact various aspects of trading, user experience, and security.
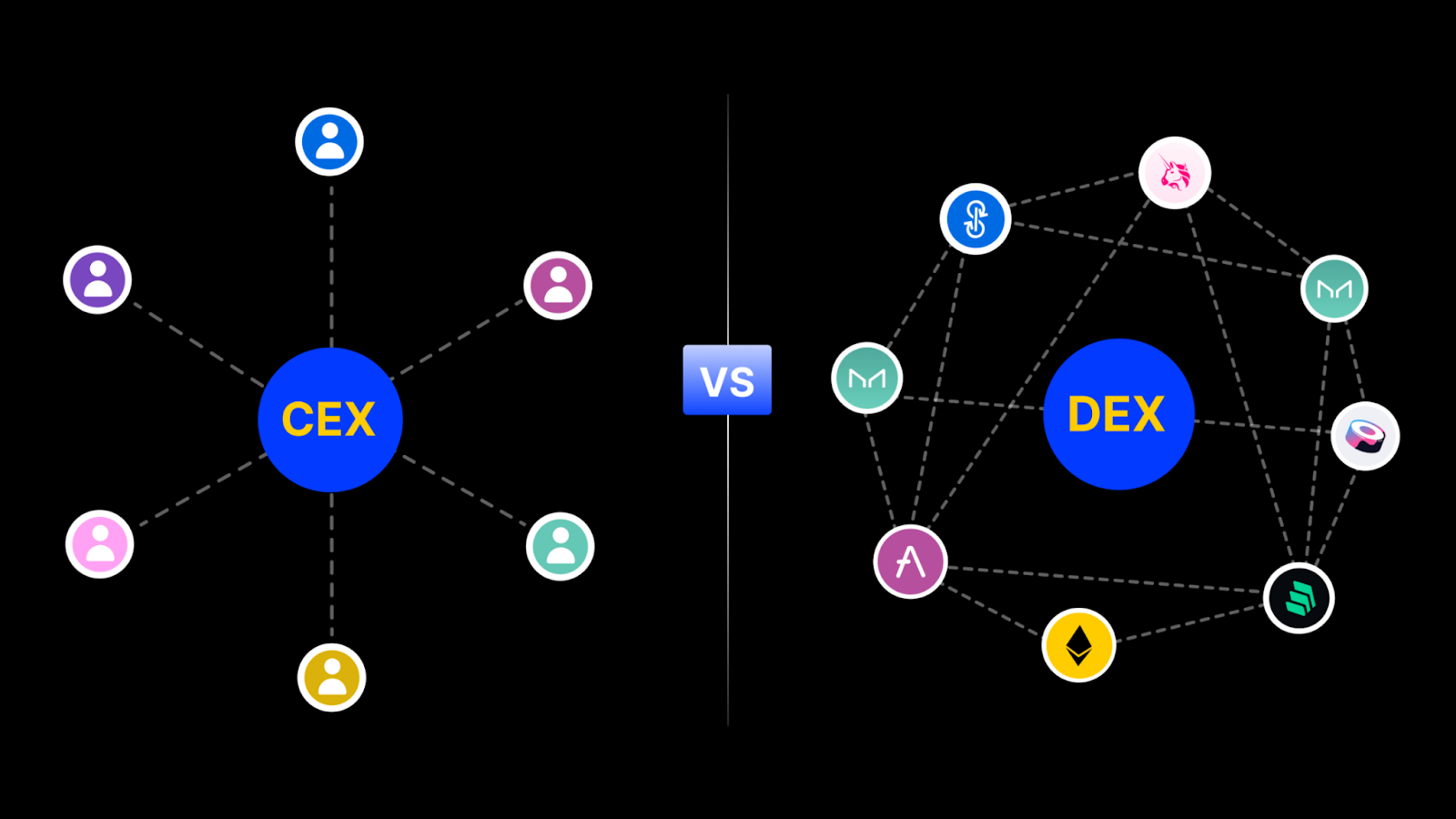
This article aims to provide detailed information about the definition as well as pros and cons of both CEX and DEX. Moreover, we also discuss further on the key differences between these two types of cryptocurrency exchange platforms. Let’s dive in!
What is Centralized Exchange (CEX)?
A Centralized Exchange (CEX) refers to a cryptocurrency exchange platform that is operated and managed by a centralized entity or organization.
In other words, it is a traditional exchange where users can buy, sell, and trade cryptocurrencies through a centralized platform controlled by a single authority. Centralized exchanges act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers, facilitating the exchange of digital assets.
Pros and Cons of Centralized Exchange (CEX)
Benefits of Centralized Exchange (CEX)
- High trading volumes and deep liquidity pools: This liquidity is essential for large trades and ensures that users can easily enter and exit positions without significant price slippage. Consequently, it allows users to execute trades quickly and at competitive prices.

- User-Friendly Interface: CEX’s interfaces offer features such as market charts, order books, and trading tools that simplify the trading process and make it accessible to a wide range of users.
- Wide Range of Assets: Many centralized exchanges support a diverse selection of cryptocurrencies and trading pairs, including major cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), and popular altcoins.
- Security Measures: Established CEX implement robust security measures to protect users’ funds and data.
- Regulatory Compliance: CEX often complies with regulatory requirements and operates within legal frameworks established by governments and financial authorities.
Disadvantages of Centralized Exchange (CEX)
- Security Vulnerabilities: CEX is susceptible to security breaches and hacking attacks, which can result in the loss of user funds.
- Lack of Privacy: CEX typically requires users to undergo identity verification and comply with know-your-customer (KYC) and anti-money laundering (AML) procedures. While these measures are intended to prevent fraud and illicit activities, they also compromise user privacy by collecting and storing sensitive personal information.
What is Decentralized Exchange (DEX)?

A Decentralized Exchange (DEX) is a type of cryptocurrency exchange platform that operates in a decentralized manner, meaning it is not controlled by any single entity or authority.
In more detail. DEX operates using smart contracts and blockchain technology to enable peer-to-peer trading directly between users.
Pros and Cons of Decentralized Exchange (DEX)
Benefits of Decentralized Exchange (DEX)
- High Level of Privacy: Many DEXs do not require users to undergo identity verification or provide personal information. This allows users to trade cryptocurrencies without disclosing sensitive information.

- Transparency: DEXs leverage blockchain technology to record all transactions on public ledgers. Users can verify the integrity of transactions and track the movement of funds in real-time.
- Lower Fees: DEXs typically have lower trading fees as they eliminate the need for intermediary services and infrastructure maintenance costs. In other words, users can save on trading fees and transaction costs.

- No Single Point of Failure: DEXs operate on distributed blockchain networks with redundant nodes. Even if some nodes go offline or are compromised, DEXs can continue to function without interruptions.
- Global Accessibility: DEXs are accessible to users worldwide, regardless of geographical location or regulatory jurisdiction.
Disadvantages of Decentralized Exchange (DEX)
- Low Liquidity: Due to the peer-to-peer nature of trading on DEXs, there may be fewer buyers and sellers compared to centralized exchanges, resulting in wider spreads and less favorable prices for traders.

- User Experience: The user experience on DEXs can be less intuitive and user-friendly compared to centralized exchanges.
- Limited Asset Selection: While popular cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum are typically available on DEXs, smaller-cap tokens and newly launched projects may have limited liquidity or may not be listed at all.
- Smart Contract Risks: While smart contracts are designed to be trustless and immutable, they are not immune to bugs, vulnerabilities, or exploits.

- Regulatory Uncertainty: DEXs operate in a regulatory gray area and may face legal challenges or regulatory scrutiny in certain jurisdictions.
- Interoperability: DEXs may need to overcome interoperability challenges to enable seamless cross-chain trading and asset transfers.
CEX Vs. DEX: Key Differences

The main differences between CEX and DEX are summarized in the table below.
| Criteria | CEX | DEX |
| Control and management | Have an overall governance structure | Are not governed by a single entity |
| Custody of Funds | Require users to deposit their funds | Do not hold custody of users’ funds |
| Trading Fees | Higher trading fees based on factors such as trading volume, order type, and membership status. | Lower trading fees |
| Interface | User-friendly interfaces | Steeper learning curve and less polished user interfaces |
| Level of Privacy | Lower Level of Privacy | Higher Level of Privacy |
| Liquidity and volume | Higher trading volumes and liquidity | Lower trading volumes and liquidity |
Which type of exchange is right for you?
Deciding if CEX or DEX is more suitable to you will be based on multiple factors. For example, individual preferences for custody, privacy, security and liquidity.
To give an instance, if you would like to have a safe and user-friendly choice for a beginner, it is highly recommended to opt for a CEX. Conversely, if you prefer an option with higher level of privacy and more control over funds, a DEX is better.
Conclusion
To sum up, choosing between a Centralized Exchange (CEX) and a Decentralized Exchange (DEX) depends on various factors, including your trading preferences, security concerns, regulatory requirements, and risk tolerance.
Therefore, it is essential for us to understand the key differences between CEX and DEX. Overall, while centralized exchanges offer liquidity, user-friendly interfaces, and regulatory compliance, decentralized exchanges prioritize decentralization, security, and user control.
About Herond Browser
Herond Browser is a Web browser that prioritizes users’ privacy by blocking ads and cookie trackers, while offering fast browsing speed and low bandwidth consumption. Herond Browser features two built-in key products:
- Herond Shield: an adblock and privacy protection tool;
- Herond Wallet: a multi-chain, non-custodial social wallet.
Herond aims at becoming the ultimate Web 2.5 solution that sets the ground to further accelerate the growth of Web 3.0, heading towards the future of mass adoption.
Join our Community!