Are you usually surprised when receiving many recommendations customized to your interests when surfing the internet? The answer to this concern is the existence of web trackers. The definition of tracker is tracking technologies, which are various tools and techniques used to collect data about user behavior and interactions on the internet. This article aims to provide you with detailed definitions of common web trackers and discuss further their characteristics as well as privacy implications.
Cookies

Cookies are small pieces of data stored on a user’s browser by the website being visited. They are commonly used to remember login information, user preferences, and other settings, making the browsing experience more efficient and personalized.
There are two main types of cookies:
- First-Party Cookies: The Greeter, The Shopping Basket, The Personal Shopper, Google Analytics, etc.
- Third-Party Cookies: The Helpful Cookie, The Sales Cookie, The Bad Guy, The Shady Cookie, DoubleClick, etc.
Privacy Implications
- First-Party Cookies: Privacy implications are limited as they are specific to the website being visited. Therefore, it may be deleted, expired, or blocked by the user’s browser
- Third-Party Cookies: Privacy implication is higher because it can be used to track users across different websites.
Pixels

Pixel trackers, also known as web beacons, are tiny, invisible images embedded on a webpage. They are designed to track user activity, such as opening an email, visiting a website, or making a purchase. Pixel trackers are commonly used by advertisers, marketers, and webmasters to collect data about user behavior.
From a closer inspection, Pixel trackers are used to monitor user behavior and gather data for analytical and marketing purposes. They allow website owners and marketers to track the effectiveness of their campaigns, monitor user engagement, and collect information about user preferences.
Examples of pixel trackers include Facebook pixel, LinkedIn Insight tag, Twitter conversion tracking pixel, etc.
Privacy Implications
Privacy implications are limited as pixels typically only track specific actions, such as opening an email, visiting a website, or making a purchase. Moreover, they are typically invisible to the user because they are small (often 1×1 pixel) and transparent. Therefore, users are usually unaware that they are being tracked by pixel trackers.
Scripts

Scripts, such as JavaScript tracking code, are executed by a browser to gather various types of information, including user interactions, device information, and browsing behavior. In more detail, scripts are used to collect various types of information about users, including user interactions, device information, and browsing behavior. They are commonly used for analytics, user behavior analysis, and personalization.
Privacy Implications
Scripts can collect a wide range of information, including user interactions, device information, and browsing behavior. While they can enhance the user experience, they can also raise privacy concerns if users are unaware of the data being collected.
Local Storage

Local storage is an HTML5 feature that allows websites to store data on a user’s device. In more detail, local storage is used for storing data such as login credentials, user preferences, and other settings to provide a customized browsing experience.
Local storage itself is not a web tracker. However, it can be utilized by web trackers to store data locally within a user’s browser. While local storage has legitimate uses, some web trackers abuse this feature to store persistent identifiers or other tracking data. This can be used for targeted advertising, user profiling, and other purposes. When used for tracking, local storage can be considered a component of a web tracker.
Privacy Implications
Local storage is typically used for storing data such as login credentials or user preferences. While it can enhance the user experience, it can also raise privacy concerns if users are unaware of the data being stored.
Location Tracking
Location tracking web trackers are tools used to collect and monitor the physical location of a user. This type of tracking can be used for various purposes, such as providing location-based services, targeted advertising, and user profiling. These trackers often collect information based on the user’s IP address, GPS, or other location-based services.
Some examples of location tracking web trackers include IP Address Geolocation, GPS Tracking, WiFi-based Geolocation, etc.
Privacy Implications
Privacy implications of location tracker is moderate. To explain, location tracking can raise privacy concerns if users are unaware or have not provided consent.
Device Fingerprinting
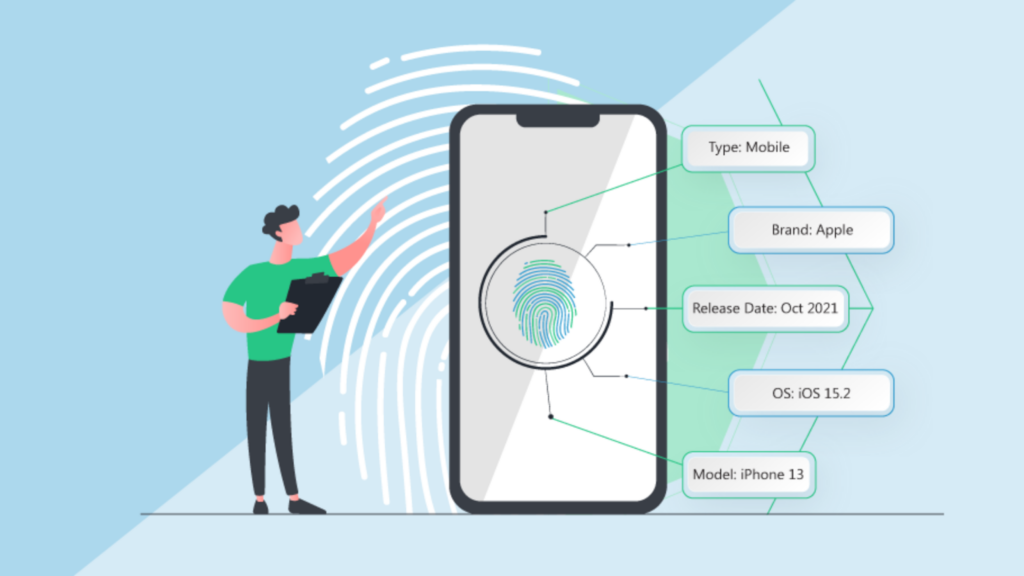
Device fingerprinting is a method used by websites and online services to collect and analyze information about a user’s device. This information is then used to create a unique identifier or “fingerprint” for that device. Device fingerprinting web trackers collect various data points, such as operating system, browser version, screen resolution, time zone, language, and installed plugins, to create a digital fingerprint of the user’s device. Generally, device fingerprinting is often used by websites and online services for various purposes, including targeted advertising, fraud prevention, and user analytics.
Here’s a description of how it works:
- Device Information Collection
- Fingerprint Generation
- Fingerprint Matching and Tracking
- Persistent Identification
Privacy Implications
Device fingerprinting can be used to track users without their knowledge. It generates a unique fingerprint of the device and browser, allowing trackers to identify and track users across different websites.
Conclusion
To sum up, these types of web trackers play a significant role in online marketing, analytics, and user experience optimization. However, it is essential to be aware of the privacy implications associated with the use of web trackers and to take appropriate measures to protect your privacy.
About Herond Browser
Herond Browser is a Web browser that prioritizes users’ privacy by blocking ads and cookie trackers, while offering fast browsing speed and low bandwidth consumption. Herond Browser features two built-in key products:
- Herond Shield: an adblock and privacy protection tool;
- Herond Wallet: a multi-chain, non-custodial social wallet.
Herond aims at becoming the ultimate Web 2.5 solution that sets the ground to further accelerate the growth of Web 3.0, heading towards the future of mass adoption.
Join our Community!