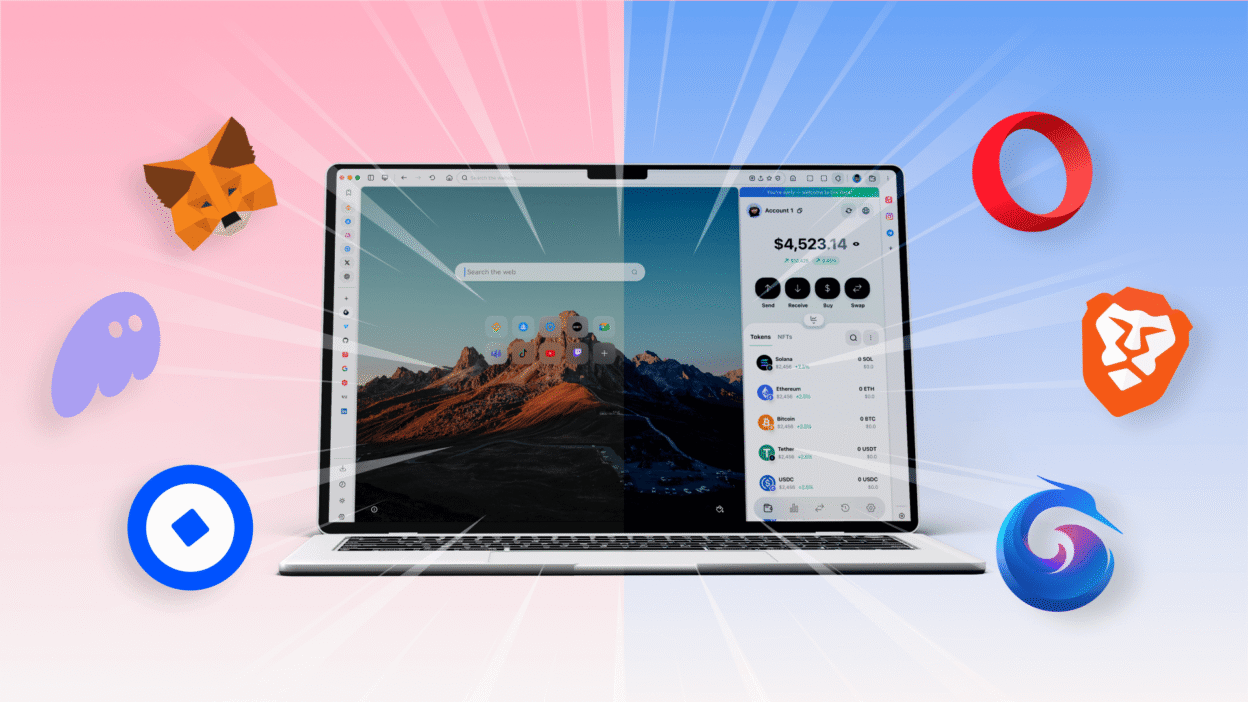
Many believe Web3 adoption is hindered primarily by scalability issues, high gas fees, or regulatory uncertainty. In truth, one of the biggest barriers remains far simpler: the user experience of crypto wallets.
For most people, a wallet is more than just a place to store assets – it’s the primary gateway to the decentralized web. Today, that gateway comes in two main forms: browser based and extension-based.
Understanding the distinctions between these approaches is essential, as they directly influence security, performance, usability, and the path to mainstream Web3 adoption.
What Is a Browser-Based Wallet?
A browser-based wallet is a cryptocurrency wallet embedded directly into a Web3-focused browser’s core infrastructure. Users don’t need to install any separate extensions (such as MetaMask, OKX, or Phantom). This native integration often delivers a more streamlined experience, with emphasis on privacy, speed, and reduced attack surfaces.
Notable examples include:
- Opera Wallet — One of the first built-in crypto wallets, now supporting multiple chains like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Solana, with features for seamless transactions and multi-account management.
- Brave Wallet — A secure, self-custodial wallet integrated into the Brave browser, inheriting Brave’s strong privacy protections (including default ad and tracker blocking).
- Herond Wallet — A keyless, multi-chain, non-custodial wallet built into the Herond Browser, designed for effortless Web3 access with enhanced security features like keyless technology

What Is an Extension-Based Wallet?
Browser extensions are small software modules that add functionality to a browser (e.g., ad blockers or password managers). An extension-based wallet operates as one of these add-ons, typically installed from marketplaces like the Chrome Web Store.
Popular examples include:
- MetaMask
- Rabby
- Phantom
- OKX Web3 wallet
To sum up, the main difference between Browser-based wallets are natively integrated into the browser for a more seamless, potentially more secure, and resource-efficient experience. Extension-based wallets, by contrast, are third-party add-ons that offer cross-browser compatibility and extensive customization but introduce additional complexity and risks.
Pros and Cons Comparison
| Browser-Based Wallet | Wallet-Based Wallet | |
| Pros | Stronger Security: Natively integrated into the browser, requires fewer broad permissions than extensions, significantly reducing phishing and malware risks. Better Performance: No additional background software lowers CPU/RAM usage, faster browsing and smoother dApp/transactions. Convenience: No installation needed; everything is ready inside one browser Privacy-Focused: Often paired with built-in ad/tracker blocking (like Brave or Herond), protecting user data by default. | High flexibility: Works across multiple browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Edge, etc.) and easy to move between devices. Flexible customization: Supports many chains, custom RPCs, hardware wallet integration, and huge developer communities (e.g., MetaMask Snap). |
| Cons | Limited flexibility: Locked to a specific browser; switching browsers usually requires exporting/importing keys. Dependent on browser updates: Wallet features may lag if the browser team prioritizes other areas. | Higher security risks: Requires extensive permissions, making extensions prime targets for phishing, fake extensions, and malware attacks. Performance impact: Background processes can slow down the browser and consume more resources. |
Both wallet types serve important roles in the Web3 ecosystem, and the best choice depends on your priorities. Extension-based wallets excel in flexibility, cross-browser support, and advanced customization—making them ideal for power users, multi-chain traders, and those who frequently switch devices or browsers.
Browser-based wallets, however, offer a cleaner, more integrated experience with potentially stronger security and performance defaults—especially appealing for users seeking simplicity, enhanced privacy, and a smoother bridge between everyday browsing and decentralized applications.
As Web3 evolves, the wallet experience will remain a critical factor in driving mass adoption. Choosing the right model can make the difference between friction-filled exploration and effortless participation.
About Herond
Herond Browser is a cutting-edge Web 3.0 browser designed to prioritize user privacy and security. By blocking intrusive ads, harmful trackers, and profiling cookies, Herond creates a safer and faster browsing experience while minimizing data consumption.
To enhance user control over their digital presence, Herond offers two essential tools:
- Herond Shield: A robust adblocker and privacy protection suite.
- Herond Wallet: A secure, multi-chain, non-custodial social wallet.
As a pioneering Web 2.5 solution, Herond is paving the way for mass Web 3.0 adoption by providing a seamless transition for users while upholding the core principles of decentralization and user ownership.
Have any questions or suggestions? Contact us:
On Telegram https://t.me/herond_browser
On Discord https://discord.gg/Herond-Browser
DM our official X @HerondBrowser